辛伐他汀透過保護粒線體對抗血管緊張素II所引發的心臟衰竭
在常見的心血管疾病包括「心臟衰竭」,通常伴隨著有粒線體功能障礙的情形。而羥甲基戊二酸單醯輔酶A還原酶(他汀類藥物)能夠抑制有害的氧自由基的產生,因此在慢性心臟衰竭中具有心臟保護作用。但是,他汀類藥物在心臟衰竭過程中是如何達到效果的? 以及對於心肌細胞內的能量提供的來源「粒線體」是否也有保護作用?這是我們研究團隊欲探索的項目。
透過心衰竭大鼠的動物實驗方式,我們團隊將大鼠分成: 1) 給予血管緊張素II(1.5 mg / kg /天/14天。2)予血管緊張素II合併給予辛伐他汀組(口服,10 mg/kg)經治療14天後在接下來的14天中停止給藥,終止實驗。
我們的研究成果發現:血管緊張素II會促進細胞內氧自由基的生成進而降低了粒線體的膜電位,導致粒線體的失能或是被破壞。然而透過給予辛伐他汀能夠有效地避免胞內氧自由基的生成進而維持了粒線體的膜電位使粒線體不致失能。而其中的關鍵在於辛伐他汀能夠在粒線體受損透過溶酶體將脂質油滴分解成脂肪酸產生能量,讓細胞有機會透過細胞自噬體來將受損的粒線體修復、或是移除。進而保護並維持細線體的功能,減緩心臟衰竭過程中對於心肌細胞的傷害。
圖形摘要
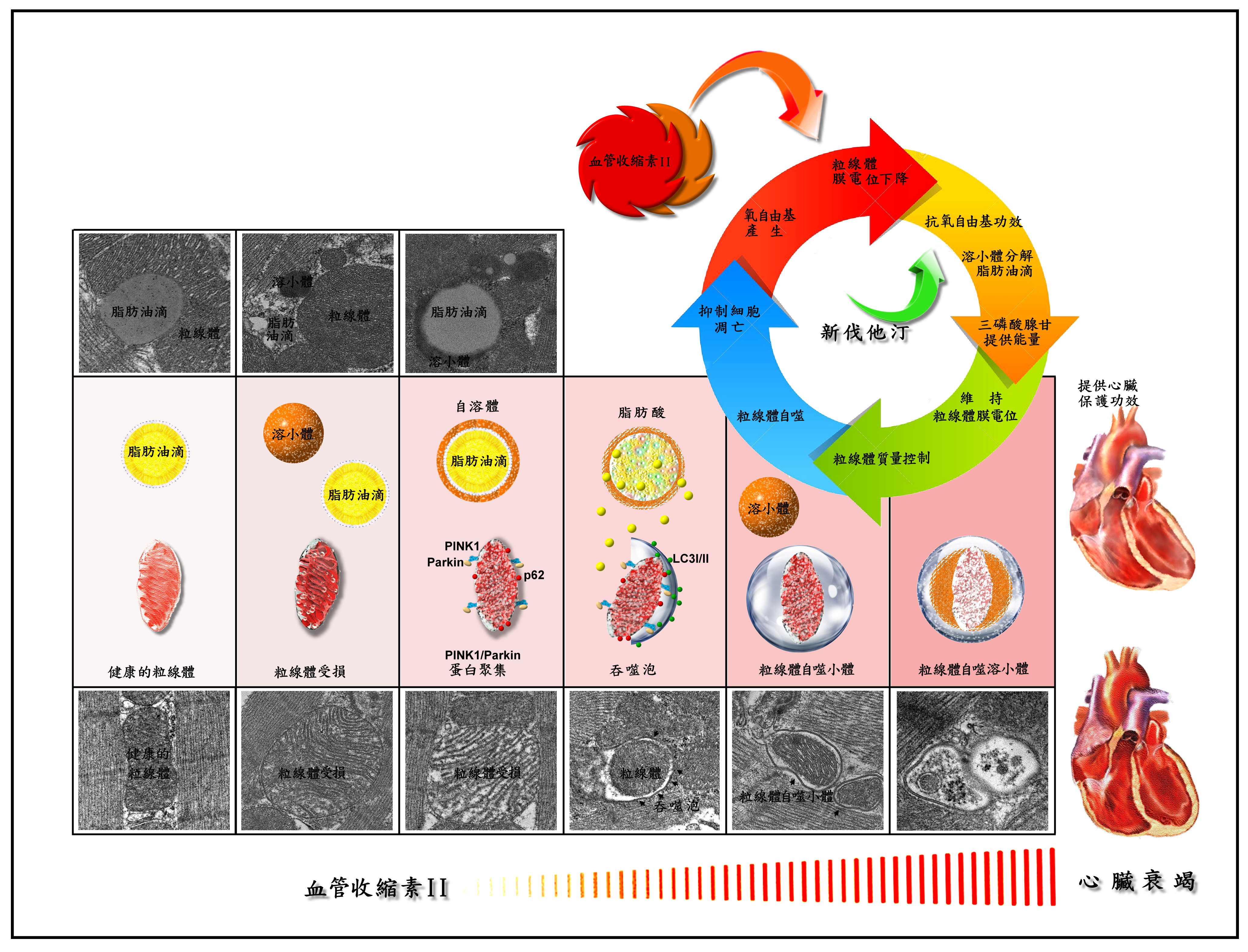
圖片說明: 血管緊張素II促進細胞內氧自由基的增加,降低了粒線體的膜電位,促使粒線體產生障礙無法提供心肌能量。透過給予辛伐他汀能夠有效地降低氧自由基並維持了粒線體的膜電位。同時辛伐他汀促進脂質油滴聚集於受損的粒腺體周圍並分解成脂肪酸提供粒線體透過自噬體的方式來自我修復,或是將無用的粒線體移除、進而維持細線體的功能減緩心臟衰竭對於心肌所帶來的傷害。
本篇為高雄醫學大學2019年月傑出論文10月份得獎文章,代表作者為醫學院呼吸治療學系劉博侖教授。
本校主要研究者之簡介:
論文第一作者為本校臨床醫學所博士班學生謝炯昭主治醫師,其為本校呼吸治療學系劉博侖教授所領導的團隊的一員。感謝科技部提供研究經費。
研究聯繫Email:
期刊出處:
British
Journal of Pharmacology. 2019
Oct;176(19):3791-3804.
期刊線上參閱網址:
Mitochondrial protection by
simvastatin against Angiotensin II-mediated heart failure
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
Mitochondrial dysfunction
plays a role in the progression of cardiovascular diseases including heart
failure. 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibitors (statins),
which inhibit reactive oxygen species (ROS) synthesis, show cardioprotective
effects in chronic heart failure. However, the beneficial role of statins in
mitochondrial protection in heart failure remains unclear.
EXPERIMENTAL APPROACH
Rats
were treated with Angiotensin II (Ang II) (1.5 mg/kg/day) or co-administered
simvastatin (oral, 10 mg/kg) for 14 days; and then administration was stopped
for the following 14 days. Cardiac structure/function was examined by wheat
germ agglutinin staining and echocardiography. Mitochondrial morphology and the
numbers of lipid droplets, lysosomes, autophagosomes, and mitophagosomes were
determined by transmission electron microscopy. Human cardiomyocytes were
stimulated and intracellular ROS and mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm)
changes were measured by flow cytometry and JC-1 staining, respectively.
Autophagy and mitophagy-related and mitochondria-regulated apoptotic proteins
were identified by immunohistochemistry and western blotting.
Graphical Abstract
This
article-“Mitochondrial protection by simvastatin against angiotensin
II-mediated heart failure” , written by Rept. Author Professor Po-Len Liu
from Department of
Respiratory Therapy in College of Medicine,,
is presented for Kaohsiung Medical University 2019 Monthly Excellent Paper
Award in Oct.
Main researcher Intro.
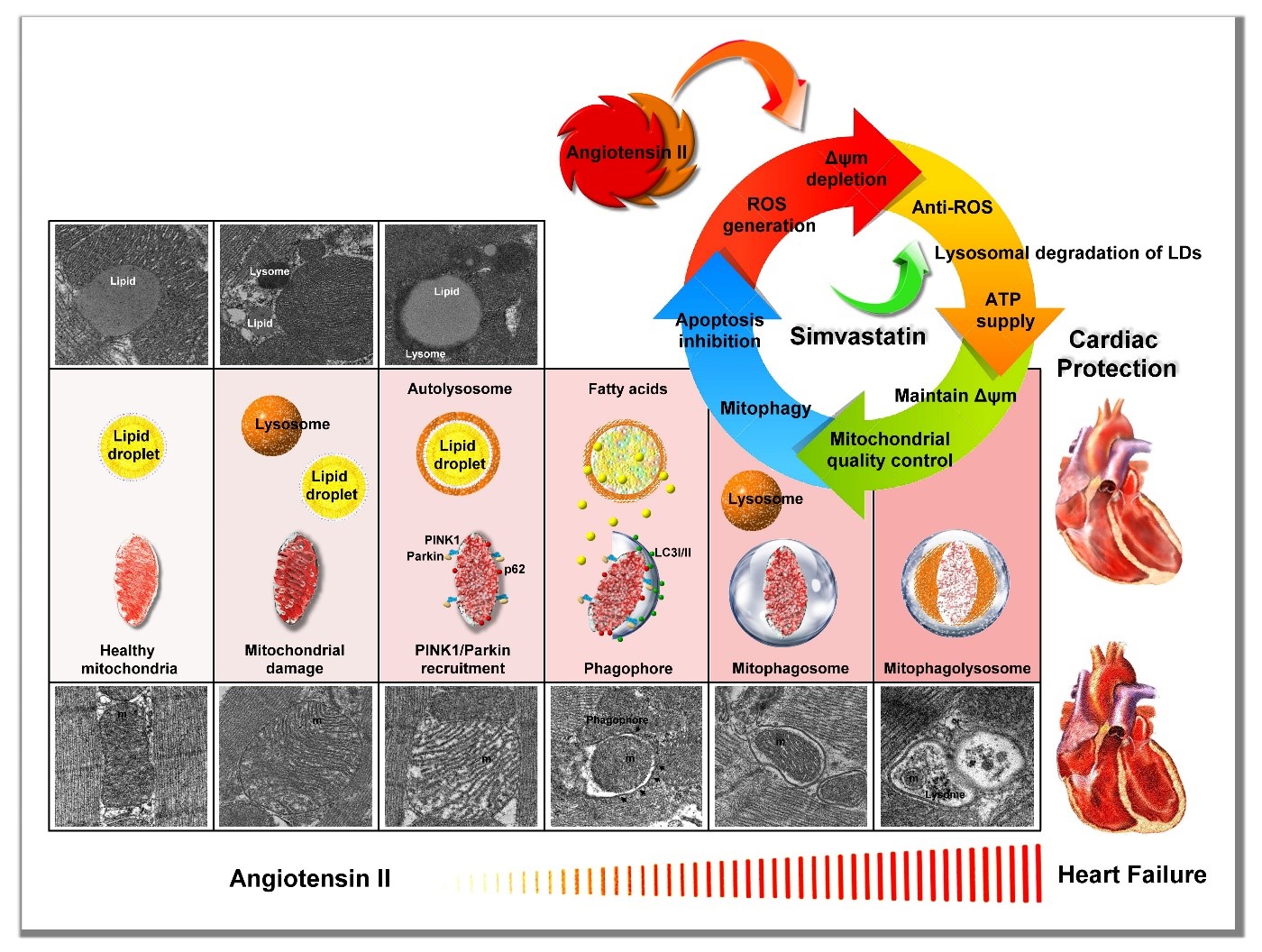
Summary
scheme of the mitochondrial protection mechanism of simvastatin in Ang
II-induced HF. Simvastatin might reduce ROS generation, regulate LDs and
lysosome levels to provide energy to maintain ΔΨm, regulate
mitochondrial quality control to promote mitophagy, and prevent
mitochondrial-regulated apoptosis.
Researcher
The first author of the paper is the attending
physician Chong-Chao Hsieh, a student of the School of Clinical Medicine,
and a member of the team led by Professor Po-Len Liu of the Department of
Respiratory Therapy, College of Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University. Thanks
to the Ministry of Science and Technology for providing research funding.
Author Email
Paper cited from:
Paper online website

