人類幹細胞研究顯示體顯性多囊腎基因突變導致心臟血管問題
臺灣是全世界腎衰竭發生率及盛行率最高的國家,體顯性多囊腎(俗稱泡泡腎),是腎衰竭第四大病因,是最常見導致腎衰竭的遺傳性腎臟病,盛行率約1:400-1:1000,佔台灣洗腎病患的2.3 %,有一半的機會會傳給下一代,心臟血管併發症是多囊腎患者最重要也是最常見的死因,目前仍無有效的治療。
「利用人類誘導性多潛能幹細胞(iPSC)研究」
人類疾病研究及治療突破不易,常受限於組織細胞取得不易及動物和人類的差異,人類iPSC是日本山中伸彌教授於西元2007年發表,2012得到諾貝爾生醫獎,因幹細胞科學的發展,本研究是將患者的血球細胞產製為iPSC,利用其多潛能的特性,將幹細胞分化為類心肌細胞來做研究。
「體顯性多囊腎基因突變導致心肌細胞電生理變化」
體顯性多囊腎病患之iPSC-CMs和由正常株iPSC所產製的心肌細胞(Control-CMs)相比較,病患的iPSC-CMs細胞內的肌漿網狀體的鈣離子含量較少。本實驗由PKD2病患的iPSC-CMs記錄到的自發性的動作電位,具有較慢的跳動速率及較長的動作電位持續時間。以L-型鈣離子阻斷劑做測試,PKD1病患的iPSC-CMs和Control-CMs具有相類似的、和劑量成正比的、縮短phase 2再極化時期的反應,且會導致細胞跳動的速率增加。PKD1病患的iPSC-CMs同時具有較不穩定的基準線,有較高比例的細胞發生延遲後去極化(DADs)。此外,PKD1及PKD2病患的iPSC-CMs相較於Control-CMs,發生更高比例的β腎上腺素受體刺激劑誘發的DADs。
綜合而言,運用電生理的實驗方法發現,體顯性多囊腎病患iPSC衍生的心肌細胞,自發性的動作電位、跳動速率、及對藥物的反應,與原病患臨床紀錄近似。體顯性多囊腎病患iPSC所衍生的心肌細胞有較高比例發生延遲後去極化,具有心律不整的傾向。依此結果推測,多囊腎的基因突變可能和多囊腎患者的心臟血管併發症相關。
「目前研究進展及未來方向」
本研究團隊在臨床上,已經開始進行多囊腎病患的世代研究,會收案多囊腎患者做基因診斷及更詳細的心臟及血管方面的評估,以釐清臨床關聯並可早期治療; 實驗室部分,研究團隊繼續以iPSC幹細胞研究,並運用 CRISPR-Cas9技術產製校正株,持續進行疾病機轉的研究及發展治療。
經費來源:科技部,中央研究院,高雄醫學大學附設醫院,高雄醫學大學,國家衛生研究院
圖形摘要
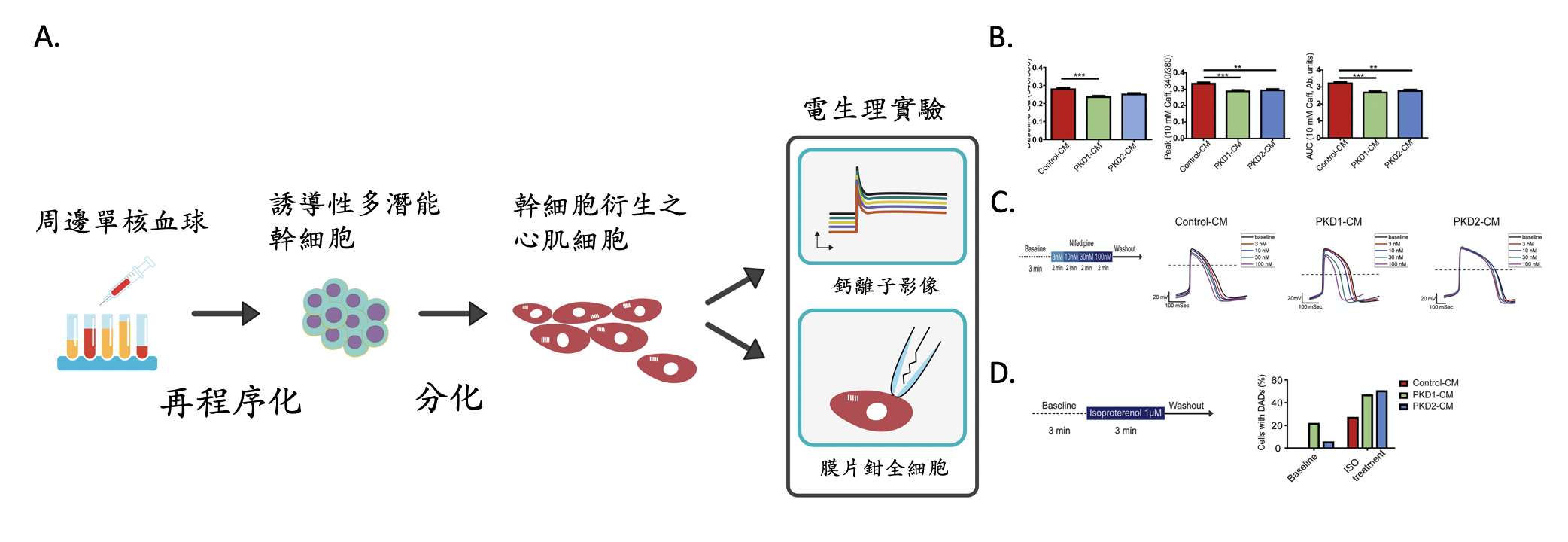
圖示:A.研究方法簡圖,將體顯性多囊腎病患的血球細胞,經過再程序化的過程產製為誘導性多潛能幹細胞(iPSC),再將iPSC分化衍生出類心肌細胞,以鈣離子影像及膜片鉗全細胞記錄做電生理的實驗及研究。B. 鈣離子影像實驗顯示病患的iPSC-CMs細胞內的肌漿網狀體的鈣離子含量較少。C. 病患iPSC-CM對鈣離子阻斷劑的反應不同。D.病患iPSC-CM較易被腎上腺素受體刺激劑誘發的發生延遲後去極化。
本校主要研究者之簡介:
本文第一作者李佳蓉助理教授接受中研院謝清河教授及高醫陳鴻鈞教授指導,於高醫中研院研讀並完成轉譯醫學博士學位學程,主要研究主題為:人類誘導性多潛能幹細胞、體顯性多囊腎、腎臟學。
研究聯繫Email:
李佳蓉
期刊出處:
EBioMedicine. 2019 Feb;40:675-684.
期刊線上參閱網址:
New finding revealed by iPSC derived cardiomyocytes suggest the direct link of ADPKD mutation genes to cardiovascular complication
Taiwan has the worldwide highest incidence and prevalence of end-stage renal disease. Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD), is the 4th leading cause of renal failure and is a hereditary kidney disease. Patients of ADPKD suffered from bilateral enlarged kidney with numerous cysts and progressive kidney failure. Cardiovascular complication represents the major cause of ADPKD patients’ mortality. Till now, we still have no effective therapy for ADPKD and its complications.
Research group by Dr. Jia-Jung Lee, Professor Chen of Kaohsiung Medical University and Professor Hsieh of Academia Sinica applied the advanced technology of human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC). They firstly generated ADPKD patient-derived iPSC as an important seed for exploring and dissecting this complicated, multiple-organ involved disease.
In the article published in EBioMedicine February 2019, the research group firstly identified the proarrhythmia phenomenon of ADPKD. The calcium image study showed altered calcium handling of the ADPKD iPSC derived cardiomyocytes. Further electrophysiological experiments with whole cell patch clamping revealed remarkable similarity of spontaneous beating pattern and the drug responsiveness of the ADPKD iPSC derived cardiomyocytes with their donors. More importantly, both ADPKD lines had proarrhythmia characteristics elicited by beta-adrenergic agonists. Taken together, the results from the ADPKD patient-specific iPSC suggested possible direct links of the mutation genes with the cardiovascular complication of ADPKD patients.
Our result pave the way to comprehensively evaluate the cardiac manifestation of ADPKD population. The research team are continuing in studying the mechanism of the mutation genes leading to the cardiac manifestation. The cell renewal and pluripotency characteristics of iPSC are promising in establishing human cell-based, in vitro disease models, drug screening platforms, and developing effective novel therapies in the anticipated future.
Fund: Ministry of Science and Technology, National Health Research Institutes, Academia Sinica Program for Technology Supporting Platform Axis Scheme, Thematic Research Program and Summit Research Program, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital, Kaohsiung Medical University, Taiwan.
Graphical Abstract
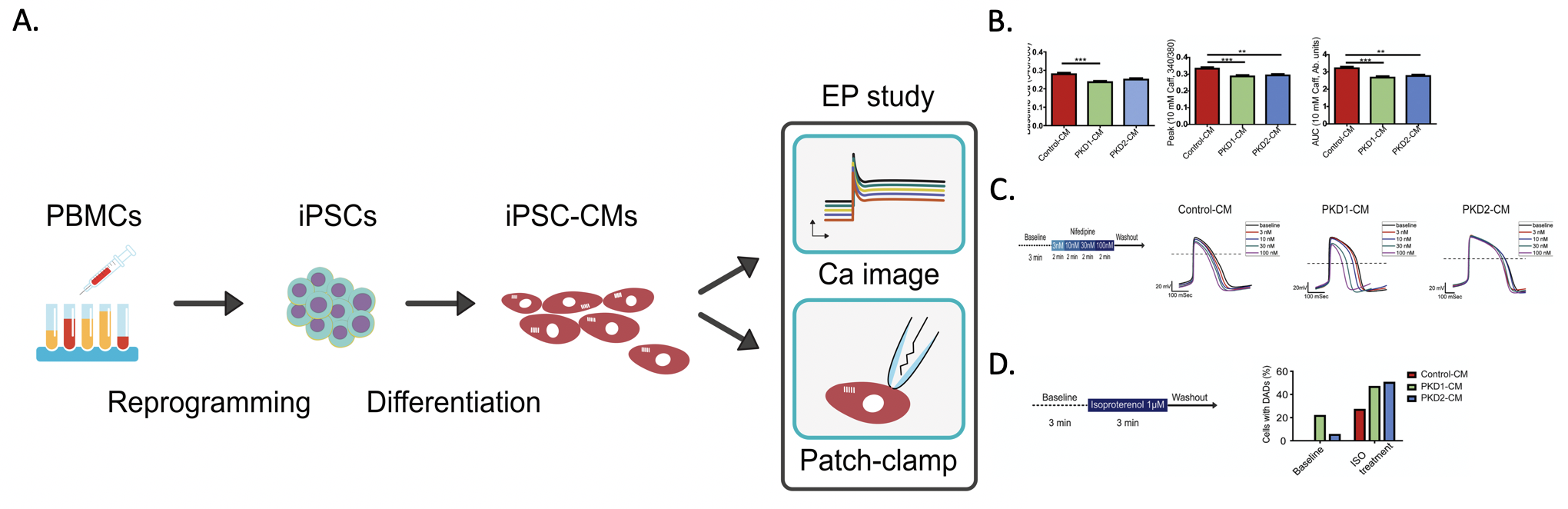
Figure: A. Schematic diagram modeling ADPKD cardiac electrical characterization with patient induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes (iPSC-CMs). B. Lower Calcium content in the patient iPSC-CMs by the calcium image study. C. Blunted response to L-type calcium channel blocker of the PKD2 patient iPSC-CMs. D. More baseline and β-adrenergic agonist-induced delay after depolarization of the patient iPSC-CM by the whole cell patch clamp study.
Main researcher Intro.
Researcher Jia-Jung Lee, M.D., Ph.D., Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital and Kaohsiung Medical University
Author Email
Paper cited from:
EBioMedicine. 2019 Feb;40:675-684.
Paper online website

