
新藥開發的寶庫-巨量植物萃取物藥庫的製備與高速篩選
天然藥物開發之困境與契機
一直以來,天然物就是藥物開發的重要來源。但隨著高通量技術的發展,新藥開發轉向了以組合化學為來源的小分子化學合成藥庫。但是過去的實務經驗中也發現:組合化學所製造的小分子化合物藥庫配合高通量篩選的策略,在先導藥物開發的成功率似乎仍無法正比於藥廠所投入的開發資源。許多大型篩選的結果令人失望,研究者也理解了「與生物活性相關的化學空間 (chemical space)多樣性」比化學藥庫的大小(化合物數量)更為重要。分析2001-2019年FDA所通過的新藥物會發現,純化學合成的小分子新藥比率為24.6%;相對的,天然物、天然物衍生物或是藥效基團(pharmacophore)的結構是來自或是源自於天然物的合成小分子藥物等等與天然物相關新藥,再加上植物新藥,全部的比率約占49%。這個結果也顯示天然物仍然是新藥開發中無法取代的資源。而其中一個決定性的因素就是天然物具有多樣化的藥效基團與高複雜度的立體化學。但是天然物的純化需要耗費大量的人力與時間,純化後所得到的化合物,大多也難以應付建構藥庫以及後續驗證實驗所需,因此由天然純化合物所構成的藥庫相當少見,且這些藥庫通常化合物種類都僅在數百種上下。且由於天然物的高複雜度立體化學特性,也大大降低天然物合成的產率,並大大提高合成步驟與困難度。這些因素都讓天然物新藥開發難以應用高通量篩選的模式進行。為了在化學多樣性、藥庫大小、藥庫製備的各種成本之間取得一個平衡點,折衷的觀念因應而生,研究者開始使用劃分層提取物(fractions)進行高通量篩選。將粗萃取物進一步分成數十個至上百個劃分層,由於小量製備便已足夠用於藥庫建置,從而使得規模小型化並且提高製備速度。這些藥庫也相當適合使用高通量篩選進行生物活性測試。而這樣的藥庫配合上靈敏的核磁共振技術能夠解決化合物分離和結構解析的瓶頸問題。
關於本核心平台
主要目標:提供多樣化且穩定之天然物藥庫及高通量篩選服務,發展成為一個優質的天然物新藥開發平台,為產、學界在生技醫藥領域挹注研發量能,促進台灣生物醫學領域與醫藥產業的發展。
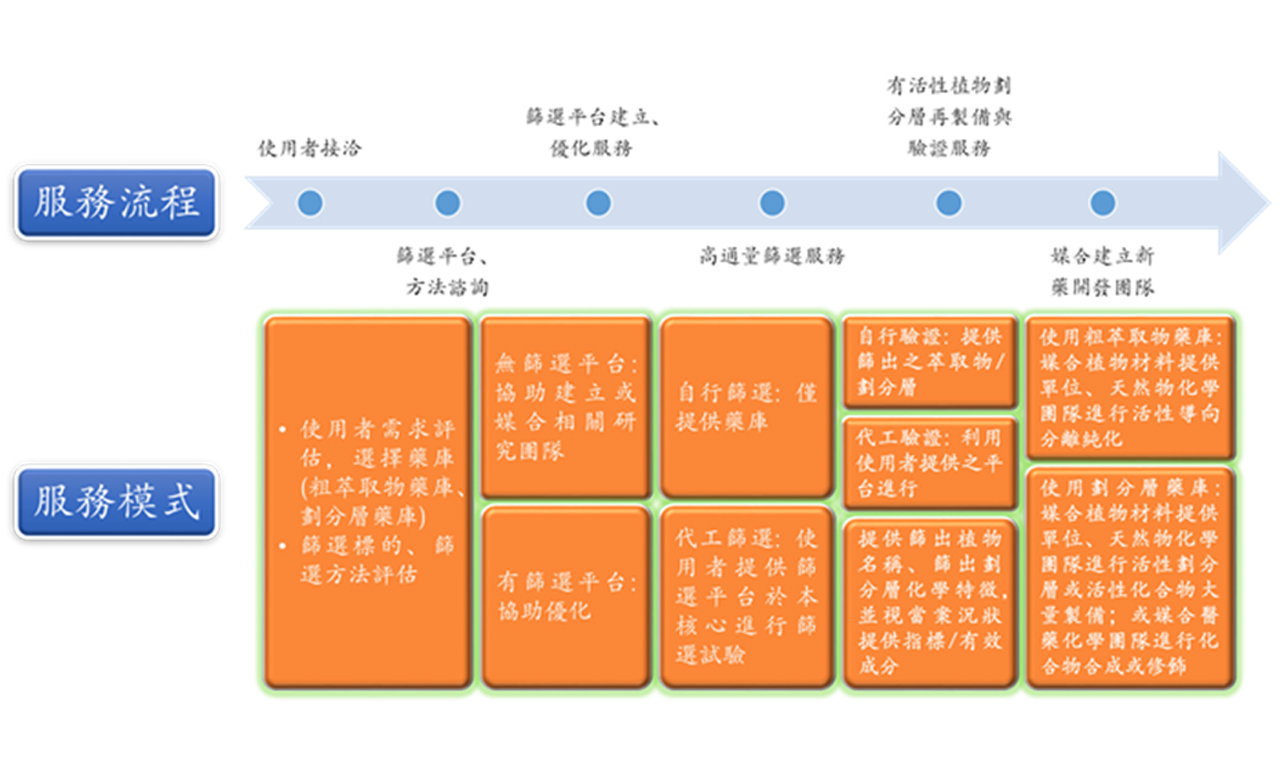
服務模式:本計畫之核心設施服務模式之規畫為整合高雄醫學大學校內現有之天然物資源與高通量篩選儀器設備,提供一站式服飾,包含使用者需求的評估、篩選標的與方法的諮詢、篩選平台的建立與優化、高通量篩選與驗證服務、活性劃分層的化學特徵及指標/有效成分的鑑定、相關研發團隊的媒合。依據使用者的需求,提出固定或客製化的服務模式。
服務能量:本資源平台目前提供3個天然物萃取物藥庫。第一個為台灣本土植物萃取物庫,目前有3,000個甲醇萃取物。第二個為辜嚴倬雲植物保種中心-辜成允植物藥庫,目前有2,889個萃取物。第三個為劃分層藥庫,目前總共有6,240個劃分層。儀器設備方面,本校已經建構有半自動化高通量篩選平台設施,包含:自動化液體工作站、自動化多功能微量盤式分析儀、高內含影像系統。我們的篩選速度大約為每天2,000~4,000個藥物/萃取物。我們能接受各種常見的篩選方法,我們的平台能偵測可見光吸收值、螢光、冷光強度值以及以螢光影像為基礎所建立之篩選方法。過去幾年我們協助使用者發現了豬籠草科與芭蕉科家族植物具有對抗B型肝炎病毒、流行性感冒病毒、以及抗癌的生物活性,已有部分成果發表,相關的專利以及後續研究目前仍正在進行中。
本校主要研究者之簡介:
核心設施負責人:天然藥物研究所顏嘉宏副教授,主要負責藥庫建置、高通量/高內涵篩選服務與推廣之相關工作。
天然物化學研發團隊:高雄醫學大學在天然物的研究領域已有悠久歷史與成果。本核心的協力研發團隊有藥學系張訓碩教授以及天然藥物研究所張芳榮教授、鄭源斌教授(現轉任職於中山大學海洋生物科技暨資源學系,此部份工作為鄭教授於高醫天然所期間所完成)。
植物樣品提供單位:辜嚴倬雲植物保種中心,執行長為清華大學生科院李家維教授。
本核心設施網址: https://nps.kmu.edu.tw/
研究聯繫Email: chyen@kmu.edu.tw
Natural Product Libraries and
High-Throughput Screening Core (NPS Core)
The difficulty and opportunity of drug
discovery from natural products
Natural
products have always been an important source of drug development. However,
with the development of HTS technology, synthetic small molecule compound
libraries which are built based on combinatorial chemistry are the main focus
of drug discovery. Combinatorial chemistry can quickly provide a large number
of small molecule compounds. However, the results of many large screens have
been disappointing in practice. It was recognized that combinatorial chemistry
techniques may not able to fulfill the expectation that could provide all the
chemicals needed for successful lead discovery. Researchers have also realized
that “chemical diversity” is more important than the size of libraries (number
of compounds). Analysis of the new approved therapeutic agents by US FDA from 2001
to 2019 revealed that 24.6% are synthetic drugs; by contrast,49% are natural
products, natural derivatives, synthetic compounds derived from natural product
pharmacophores, or botanic drugs (mixture of natural compounds). One of the
decisive factors is that natural product collections exhibit a wide range of
pharmacophores and a high degree of stereochemistry. This indicated that
natural products are still an irreplaceable resource for drug discovery. However,
it is a time- and labor-consuming work to isolate pure compounds from natural
materials; and usually only limited variety and quantities of pure compounds
are obtained. In addition, the high stereo-chemical diversity properties of
natural products also hugely increase the difficulties in synthesis of natural products.
Thus, pure compound library of natural product is not commonly available. These
factors make it difficult to apply HTS approaches for drug discovery from
natural product. In order to strike a balance between chemical diversity, drug
library size, and various costs of drug library preparation, researchers have
begun to use pre-fractioned library for HTS. A crude extract is divided into
tens to hundreds of fractions. Small quantities of crude extracts are enough
for the preparation of library with large number of fractions for biological
tests. Furthermore, the bottleneck of the isolation and structure-elucidation
of active component in fractions can also be addressed by sensitive NMR
techniques.
About
NPS Core lab
Goal: Providing diversified
and stable natural product libraries and high-throughput screening services;
and becoming a high-quality platform to help natural product drug discovery
research of academic and industrial fields.
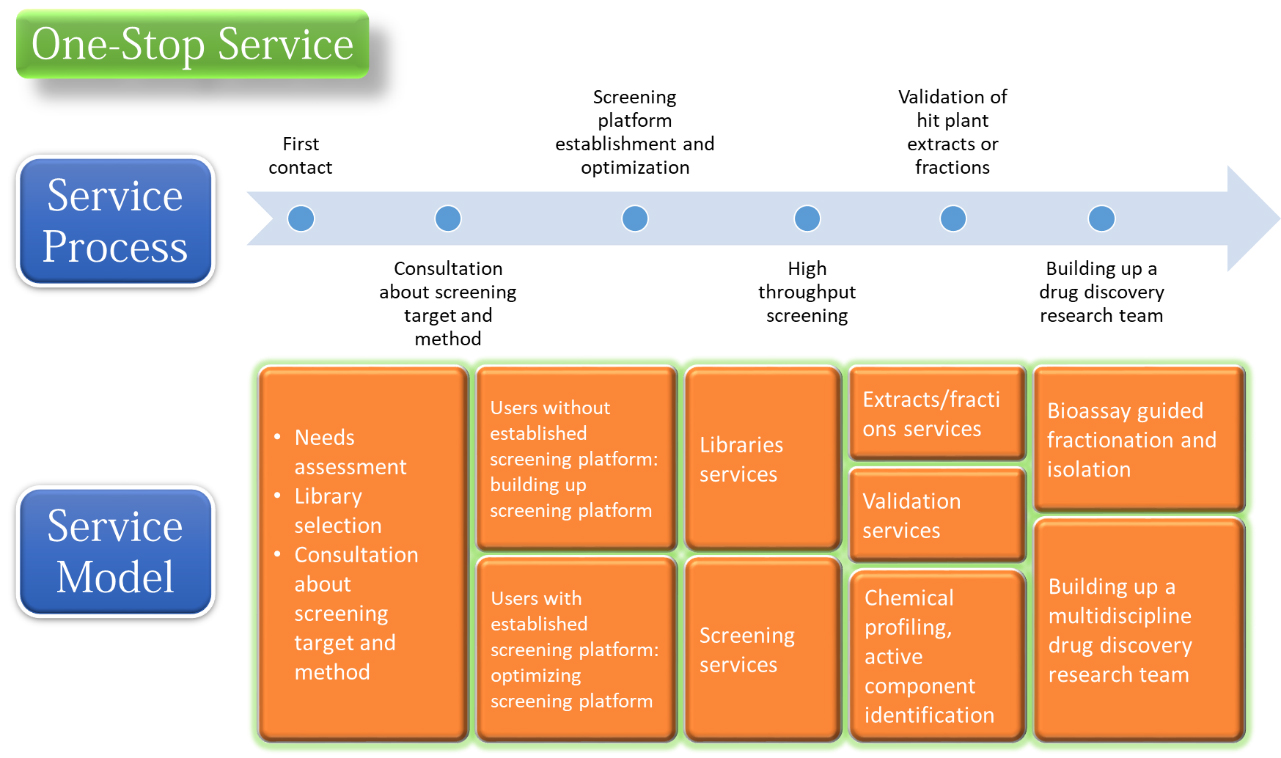
Our
service: This platform integrates the existing natural product resources and
high-throughput screening equipment in KMU. Our service starts with a
consultation with users on the ultimate goal, target and assay methods of
screening, establishment and optimization of screening assay, high-throughput
screening, hits verification, chemical characterization of active fractions,
and identification of indicators/active ingredients. We will bridge user and
our supporting laboratories to build a drug discovery research team. According
to users demand, customized services is can be integrated with our standardized
models. Our capacity: We offer three natural product libraries. The first one
is the Taiwan indigenous plant extract library, which contains extracted 3,000
extracts. The second library is Dr. Cecilia Koo Botanic Conservation Center
(KBCC)-library, which contains 2,889 extracts. The third library is
pre-fractioned library, which contains 6,240 fractions. We equipped with an
automatic liquid handling workstation, an automatic multimode plate reader, and
a high-content system. Our screening capacity is around 2,000~4,000 tests/day.
Absorbance, fluorescence, luminance, or image based assays are all applicable
on our platform.
Main researcher Intro.
PI
of NPS Core: Chia-Hung Yen, (Associate Professor, Graduate Institute of Natural
Products) who responsible for the management, construction and maintenance of
natural product libraries and high-throughput/high content screening services.
Natural
product chemistry teams: KMU has long and rich experience on natural product
research. Thus, we have strong supported labs led by Prof. Hsun-Shuo Chang at School
of Pharmacy, and Prof. Fang-Rong Chang and Prof. Yuan-Bin Cheng at Graduate
Institute of Natural Products. (Prof. Yuan-Bin Cheng currently teaches at Department
of Marine Biotechnology and Resources, National Sun Yat-Sen University.
Extracts preparation for libraries construction was carried out by Prof Cheng’s
lab in KMU)
Plant
material supporting team: Dr. Cecilia Koo Botanic Conservation Center of which
Prof. Chia-Wei Li at Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biology, National
Tsing Hua University is the CEO.
Website
of NPS Core: https://nps.kmu.edu.tw/
E-mail
address of CH Yen: chyen@kmu.edu.tw
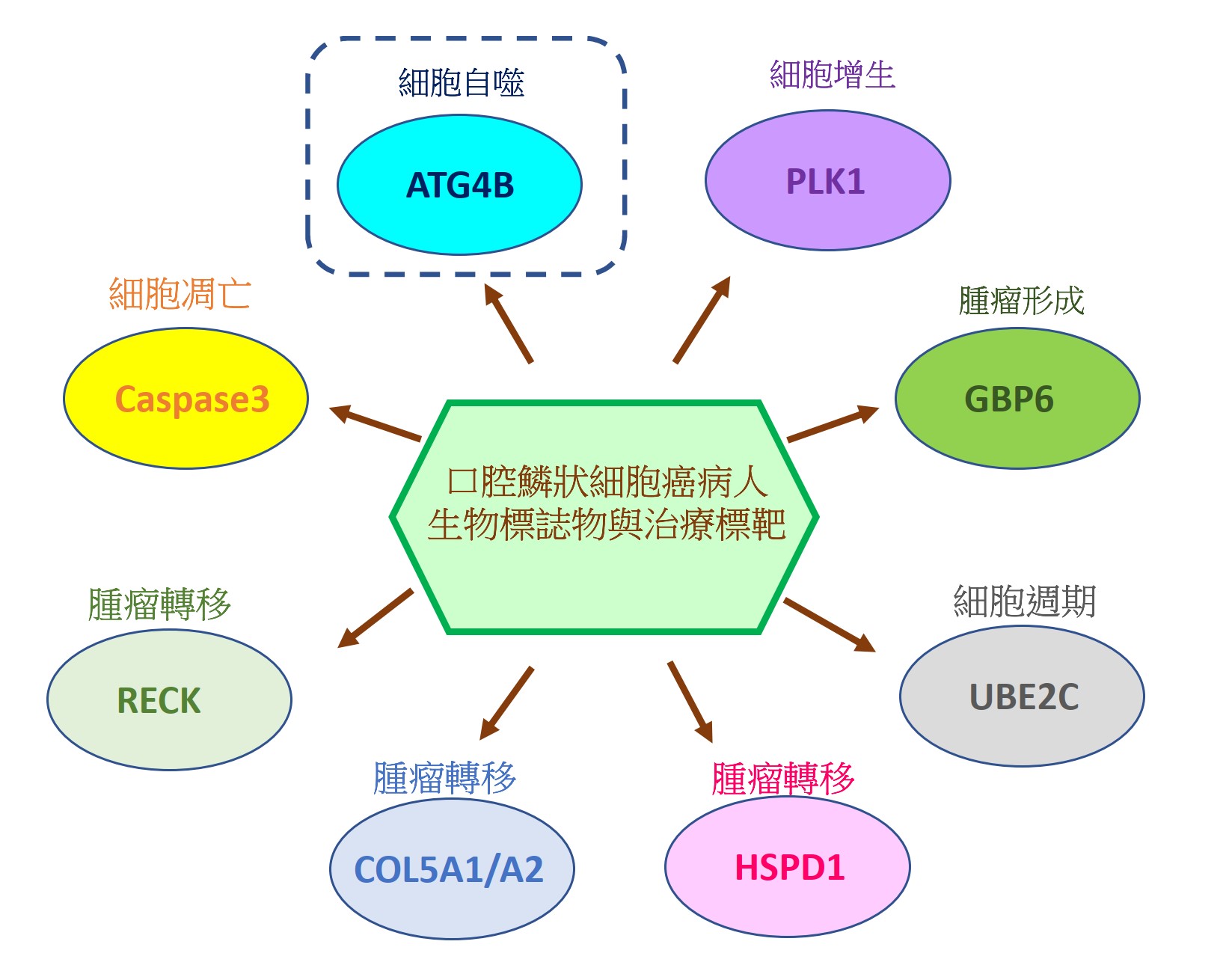
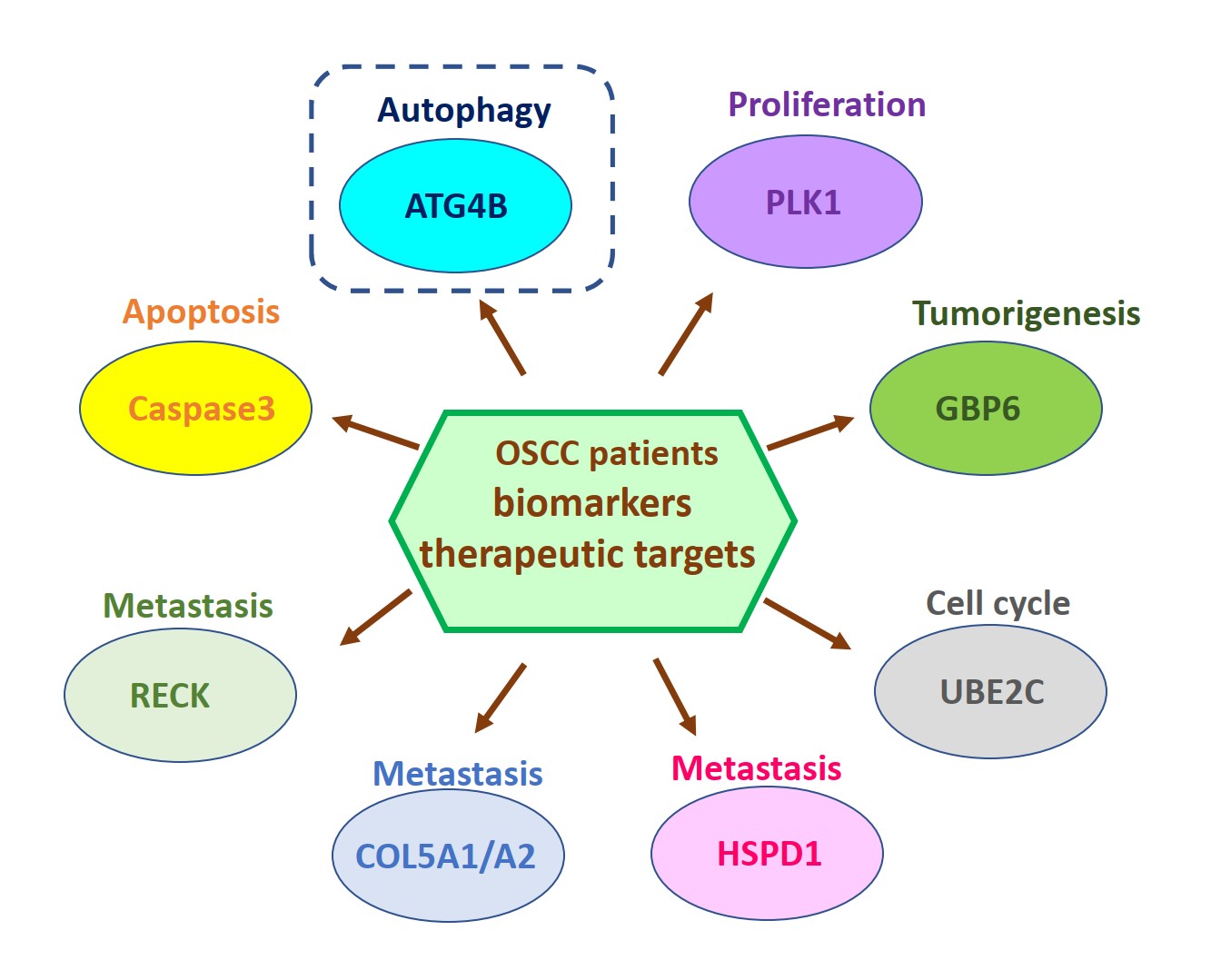
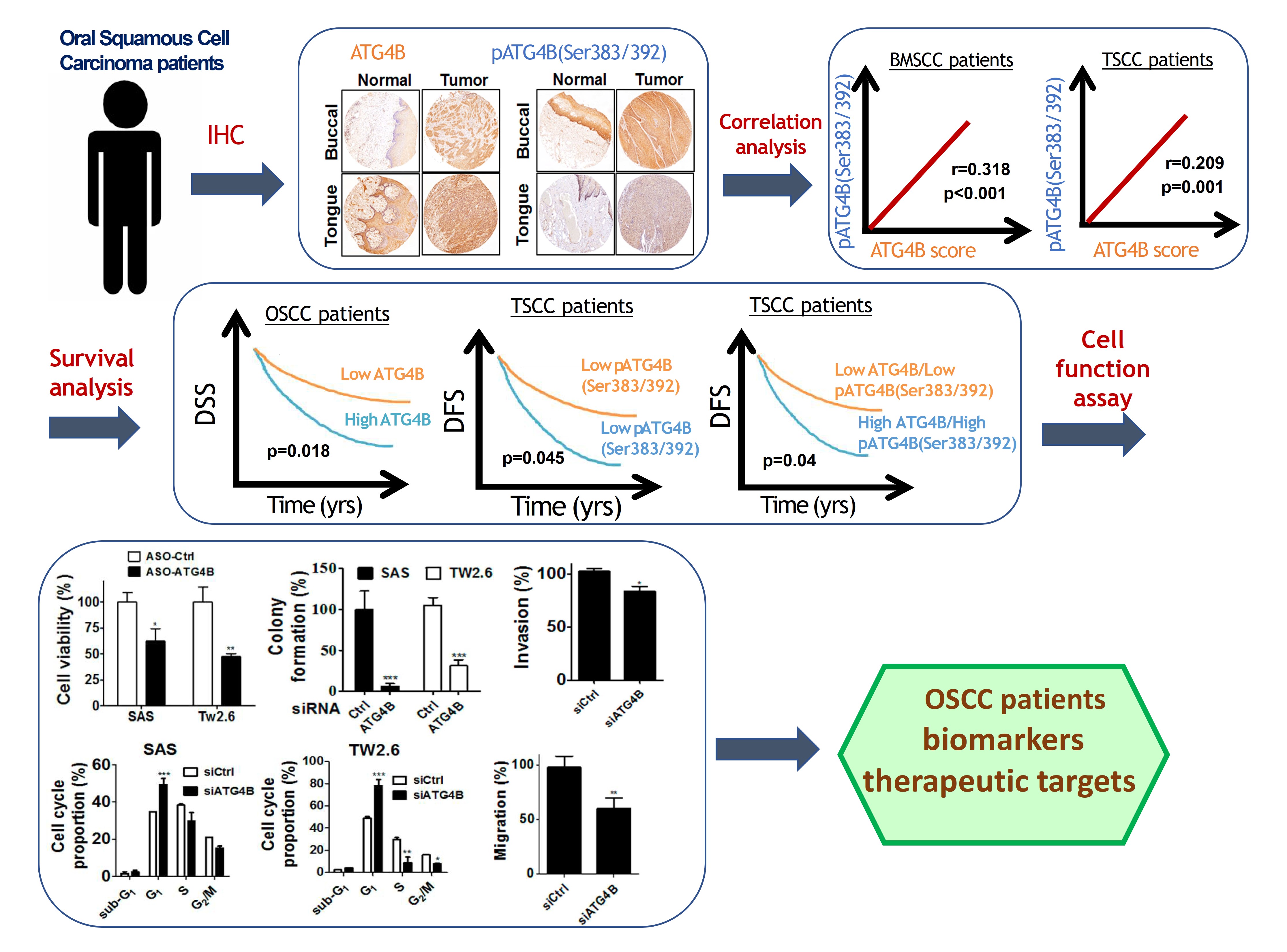
由於缺乏潛在的生物標誌物和治療靶標,導致口腔鱗狀細胞癌(OSCC)仍然是全世界癌症死亡的主要原因之一。因此,我們的研究重點放在找出具潛力的OSCC生物標誌物和治療靶標。我們已經從癌症基因組圖譜數據庫中分析口腔癌患者組織中的基因表現情形或進行siRNA庫篩選,藉由定量聚合酶鏈反應和免疫組織化學來比較OSCC患者正常及腫瘤組織中的基因表現來確認潛在的致癌基因和抑癌基因。我們還透過OSCC癌細胞和異種移植小鼠模型驗證了這些潛在生物標記物的作用和分子機制。到目前為止,我們已經發表幾篇具潛力的OSCC生物標誌物和治療靶標相關論文,如圖1所示。在這裡,我們介紹其中一個具潛力的生物標誌物和治療靶標-自噬相關蛋白酶4B(ATG4B),如圖2所示。
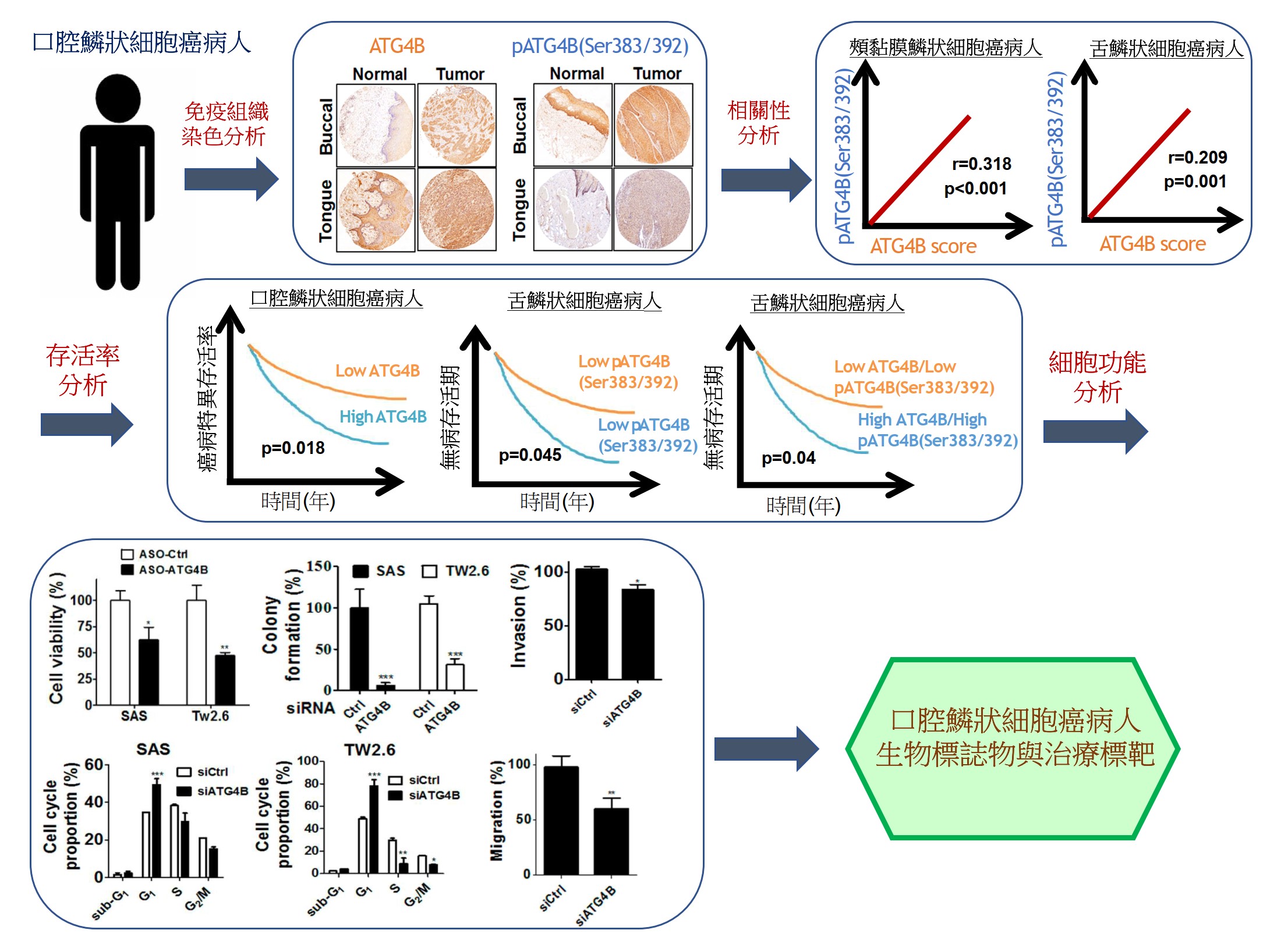
自噬相關蛋白酶4B(ATG4B)是自噬作用中不可少的蛋白酶,Ser383/392處磷酸化的ATG4B可增加其蛋白水解活性。 ATG4B的表現和活化對於癌細胞的增殖和侵襲相當重要。然而,ATG4B和Ser383/392處磷酸化的ATG4B在OSCC患者臨床之關聯性仍然未知,尤其在頰黏膜SCC(BMSCC)和舌頭SCC(TSCC)患者中。使用498例OSCC患者檢體做成組織微陣列,包括179例BMSCC和249例TSCC患者,我們發現BMSCC和TSCC患者腫瘤組織中的ATG4B和Ser383/392處磷酸化的ATG4B之蛋白表現量比鄰近組織正常中的要高。在OSCC患者中,特別是在晚期腫瘤患者中,高蛋白表現量的ATG4B與較差的疾病特異性生存率(DSS)有顯著相關。另外,Ser383/392處磷酸化的ATG4B1蛋白表現量與TSCC患者的不良無病生存率(DFS)也相關。此外,在BMSCC和TSCC患者中,ATG4B蛋白表達量與Ser383/392處磷酸化ATG4B蛋白表現量呈現正相關。然而,僅在TSCC患者中,同時高蛋白表現量的ATG4B和Ser383/392處磷酸化的ATG4B與患者較差的DFS相關,而在BMSCC和TSCC患者中,它們卻與患者DSS無顯著相關。此外,用反義寡核苷酸(ASO)或干擾RNA(siRNA)沉默ATG4B可以減少TW2.6和SAS口腔癌細胞的細胞增殖。另外,剔除口腔癌細胞的ATG4B可以減少細胞遷移和侵襲。綜上所述,這些發現顯示,ATG4B可能作為未來OSCC患者的潛在生物標誌物和治療靶標。
本校主要研究者之簡介:
劉佩芬助理教授(生物醫學暨環境生物學系)
研究聯繫Email:
pfliu@kmu.edu.tw
期刊出處:
Cancers 2019, 11(12), 1854
研究全文下載:
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) remains one of the major leading causes of cancer death worldwide due to the lack of potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Thus, our research is focusing on identifying potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for OSCC. We have analyzed the gene expression in the tissues of oral cancer patients from the Cancer Genome Atlas database or performed siRNA library screening to identify potential oncogenes and tumor suppressive genes by comparing gene expression between normal and tumor tissue of OSCC patients with quantitative polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemistry. We also verified roles and molecular mechanisms of these potential biomarkers by using OSCC cancer cells and xenografted mice models. So far, we have published several related papers with potential OSCC biomarkers and therapeutic targets, as shown in Figure 1. Here, we introduced one of the potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets-autophagy-related protease 4B (ATG4B), as shown in Figure 2.
Autophagy related protease4B (ATG4B) is an essential protease for the autophagy machinery, and ATG4B phosphorylation at Ser383/392 increases its proteolytic activity. ATG4B expression and activation are crucial for cancer cell proliferation and invasion. However, the clinical relevance of ATG4B and phospho-Ser383/392-ATG4B for OSCC remains unknown, particularly in buccal mucosal SCC(BMSCC) and tongue SCC (TSCC). With a tissue microarray comprising specimens from 498 OSCC patients, including 179 BMSCC and 249 TSCC patients, we found that the protein levels of ATG4B and phospho-Ser383/392-ATG4B were elevated in the tumor tissues of BMSCC and TSCC compared with those in adjacent normal tissues. High protein levels of ATG4B were significantly associated with worse disease-specific survival (DSS) in OSCC patients, particularly in patients with tumors at advanced stages. In contrast, phospho-Ser383/392-ATG4B expression was correlated with poor disease-free survival (DFS) in TSCC patients. Moreover, ATG4B protein expression was positively correlated with phospho-Ser383/392-ATG4B expression in both BMSCC and TSCC. However, high coexpression levels of ATG4B and phospho-Ser383/392-ATG4B were associated with poor DFS only in TSCC patients, whereas they had no significant association with DSS in BMSCC and TSCC patients. In addition, silencing ATG4B with an antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) or small interfering RNA (siRNA) diminished cell proliferation of TW2.6 and SAS oral cancer cells. Further, knockdown of ATG4B reduced cell migration and invasion of oral cancer cells. Taken together, these findings suggest that ATG4B might be a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for OSCC patients in the future.
Main researcher Intro.
Assistant Professor Dr. Pei-Feng Liu
(Department of Biomedical Science and Environment Biology)
Author Email:
pfliu@kmu.edu.tw
Paper cited from:
Cancers 2019, 11(12), 1854
Research Paper available online on website:
遊戲教學:提升醫學生的性別素養與促進同志友善醫療
醫學教育者如何善用教學方法,在教導學生專業學習之際,亦培育學生的性別素養?致力於性別與醫學教育研究的高雄醫學大學教授楊幸真,在〈教育為先:促進同志友善醫療的素養導向課程與遊戲教學〉論文中,分享如何在素養導向醫學教育觀點下,運用遊戲教學,創造一個具吸引力的教學活動,促進學生積極參與學習及提升學生的性別素養。
設計遊戲,教性別也教精神醫學
遊戲學習,是一種參與式的教育取徑,能讓學生一起腦力激盪,解決問題。該研究以精神醫學臨床教育醫學生為研究對象,設計「同志醫療與身心健康」課程及九宮格遊戲。九宮格遊戲除了做為暖身活動,引發學生學習動機外,亦做為學習評量工具,具有前測與形成性評量的功用。九宮格遊戲問題的設計,依循素養導向醫學教育的理念,從知識、態度與技能面向出題,了解學生對於同志醫療及精神健康議題方面的認識。
因為是遊戲,即使不會,也是令人愉快的挫敗感
素養,必須透過學習歷程才可能形成,無法直接灌輸。該研究從學生的回應發現,遊戲教學確實能協助教師整合性別與醫療健康照護知識於遊戲過程之中。更重要的是,對於同志醫療與健康議題而言,因為是遊戲,也較能去除學生給予政治正確的回答,能讓學生對於LGBT的認識,包括正確、錯誤、甚至是偏見,都能在遊戲過程中表露與對話,並藉由互動對話產生有意義的學習。
研究者與授課教師在設計九宮格問題時,原以為有些基本知識是學生一定知道且能夠回答的問題。但是,大多數醫學生不知道同性戀去病化是那一年,許多人不清楚何謂跨性別,以及少數人不知道LGBT代表的內涵。好的遊戲學習,具備挑戰性及令人愉悅挫敗感的特性。因為是遊戲,學生即使答不出來,也不會有挫折感。這種在遊戲之中經歷的挑戰與愉快挫敗感,反而更激發學生學習動力。如學生所言: “就更想知道其他題目是什麼”, “吸引我的注意力”,不僅對於接續的性別與精神醫學概念講解更能專注聆聽,亦達到遊戲學習「探索」的功用,激發學生願意主動思考。
此外,做為教學活動與評量工具的九宮格遊戲,還具有支持學習與教學的功用。前者能發現學生的學習困難或迷思概念,以便適時提供學習鷹架,提升效能感。例如,該課程在遊戲進行之後進行概念教學,其中就包含對於同性戀去病化歷史及LGBT的介紹。課程亦安排同志敘說自身就醫經驗,藉由真實生命經驗敘說,以回應九宮格的問題,促進知識、態度與技能的統整學習。後者乃指遊戲的設計,易讓教師將評量融入教學,使評量成為教學方法與教學活動的一部分,而不是外加於教學的評價工具。
學習成效的提升,必得有策略地運用教學方法
該研究發現,遊戲讓學生有參與感,有效提升學生的學習動機及助益主動學習及知識探索。遊戲同時做為教學活動與評量工具,能落實素養導向教育重視學習過程中的評量與立即回饋。運用遊戲教學,確實能有效引領醫學生學習性別,促進將性別知識、態度與技能等多元能力統合納入精神醫學教育與學習之目標。
本校主要研究者之簡介:高雄醫學大學性別研究所教授楊幸真
研究聯繫Email: yhc@kmu.edu.tw
期刊出處:
Yang, H. C. (2019). Education first: Promoting LGBT+ friendly healthcare with a competency-based course and game-based teaching. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(1), 107; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010107
研究全文下載:https://reurl.cc/Y6dxEO
Game-Based Teaching: Enhancing Medical
Students’ Gender Competency and Promoting LGBT Friendly Healthcare
How can medical educators make good use
of teaching methods to cultivate medical students’ gender competency while
teaching students psychiatry and healthcare education? Yang Hsing-Chen, a
professor at Kaohsiung Medical University(KMU), who is devoted to the study of
gender and medical education, responded to this question in her paper
“Education First: Promoting LGBT Friendly Health Care with a Competency-Based
Course and Game-Based Teaching.” Using the competency-based medical education
(CBME) perspective and gender courses in psychiatric clinical education, this
research paper explored whether the application of game-based teaching
activities can promote gender learning and improve the gender competency of
students.
Design games to teach gender and
psychiatry
Game-based teaching and learning is a
participatory educational approach in which students brainstorm together to
solve problems. The research course, LGBT Health and Medical Care (LGBT HMC) was
added to KMU psychiatric clinical education training for one academic year.
According to the competency-based course and teaching design ideas, a 3 ×
3-grid game was designed as the warm-up game for LGBT HMC. Apart from
stimulating learning motivation, this game served as an evaluative tool,
functioning as a pretest and formative evaluation. The aim of this game was to
prompt learning motivation. It was designed to assess students’ prior LGBT
knowledge–, which provided feedback informing the adjustment of the course and
the improvement of learning conditions. Those questions of the 3 × 3 grid game
were designed to elicit responses regarding students’ understanding of LGBT
health care and mental health issues and could be answered from the
perspectives of knowledge, attitudes, and skills.
“It’s a game, even if you don’t know
the answer, it’s a pleasant frustration”
Using the 3 × 3 grid game as the
teaching activity aimed to achieve two objectives: to trigger the learning
motivation of students and encourage them to proceed to concept learning and to
prevent lecturing on LGBT concepts from becoming an instance of the “banking
education.” Because competency can only be formed through learning processes
rather than through direct inculcation. Student responses revealed that
game-based teaching can help teachers to convey and integrate gender and
medical knowledge or concepts into a game; students can connect with the course
content and experience knowledge transformation to achieve positive learning
outcomes. With respect to LGBT medical and health care issues, within the
context of a game, students were able to express and discuss their correct,
incorrect, or even biased understanding regarding LGBT communities without
being overly concerned with providing politically correct answers. These
interactions and dialogues led to meaningful learning.
When Professor Yang and her researcher
team and the teachers were designing the questions for the 3 × 3 grid game, the
answers to some of the questions were considered basic knowledge that students
must know and be capable of understanding. Surprisingly, none of these
students, who had already commenced their internships in a hospital, could
state the year in which homosexuality was removed from the classification of
mental diseases. Numerous students did not know what “transgender” meant, and a
few students were unfamiliar with the meaning of LGBT. As previously stated,
successful game-based learning is adequately challenging and pleasantly
frustrating. Experiencing challenges can also be positively stimulating in a
game and provoke learning motivation among students; for example, one student
stated that “You become curious about what the other questions are, and that
draws my attention.” The students were more focused and invested in the
following section of the course, which explained the concepts of LGBT health
issues and psychiatry. The game achieved the exploratory function of game-based
learning and provoked active thinking in students.
This study revealed that the 3 × 3 grid
game, which served as the teaching activity and assessment tool, also supported
learning and teaching. The game helps with learning by identifying difficulties
and misconceptions experienced by students, and this enables the timely
provision of instructional scaffolding to enhance efficacy. For example, the
course was designed to conduct concept teaching after the game, and the
concepts included the history of the removal of homosexuality from the
classification of mental diseases and an introduction to LGBT communities. The
teachers also invited LGBT individuals to the class to share their own medical
experiences. These real-life experiences gave the answers to the questions in
the game and helped the students with the integration of knowledge, attitudes,
and skills. In addition, the game helps teaching because the design of the game
facilitates the integration of assessment into teaching, which makes the
assessment part of the teaching method and teaching activity rather than a
supplementary evaluative tool. In fact, both aspects of the game can enhance
assessment for teaching and exhibit the value of the instant feedback obtained
in CBME and game-based learning.
Use teaching
methods strategically to improve learning effectiveness
The findings of this study were as
follows: (1) Games encouraged student participation and benefited gender
knowledge transmission and transformation through competency learning. (2)
Games embodied the idea of assessment as learning. The enjoyable feeling of
pressure from playing games motivated students to learn. Using games as both a
teaching activity and an assessment tool provides the assessment and instant
feedback required in the CBME learning process. In short, game-based teaching
successfully guides medical students to learn about gender and psychiatry
and achieve the learning goal of
integrating knowledge, attitudes, and skills.
Main
researcher: Professor Hsing-Chen Yang,Graduate Institute of Gender Studies,
Kaohsiung Medical University
Author
Email: yhc@kmu.edu.tw
Paper
cited from:
Yang, H.
C. (2019). Education first: Promoting LGBT+ friendly healthcare with a
competency-based course and game-based teaching. International Journal of
Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(1), 107; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010107
Research
Paper available online on website: https://reurl.cc/Y6dxEO
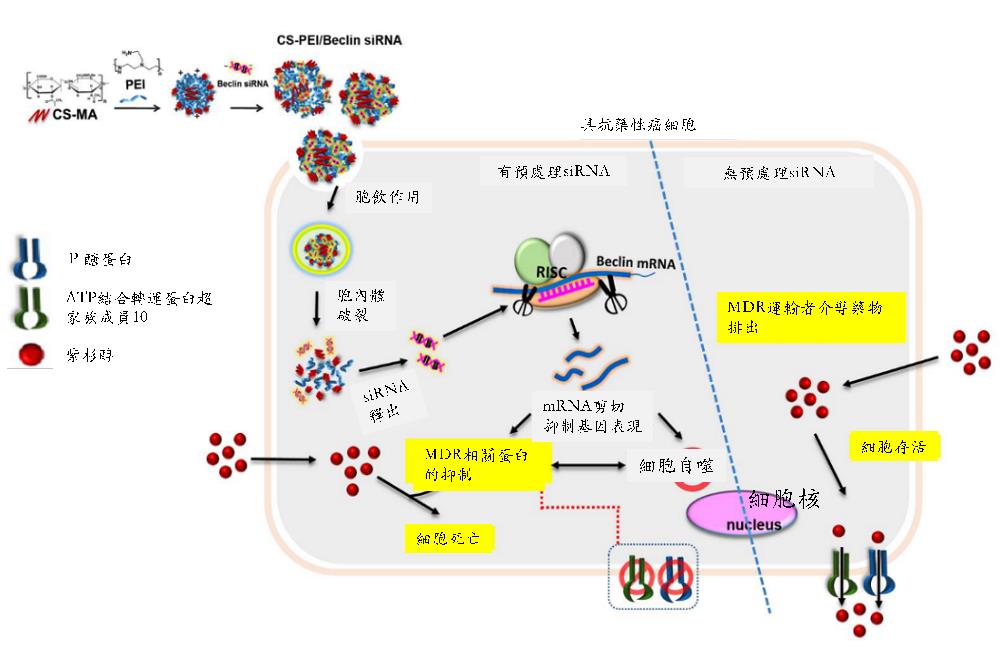
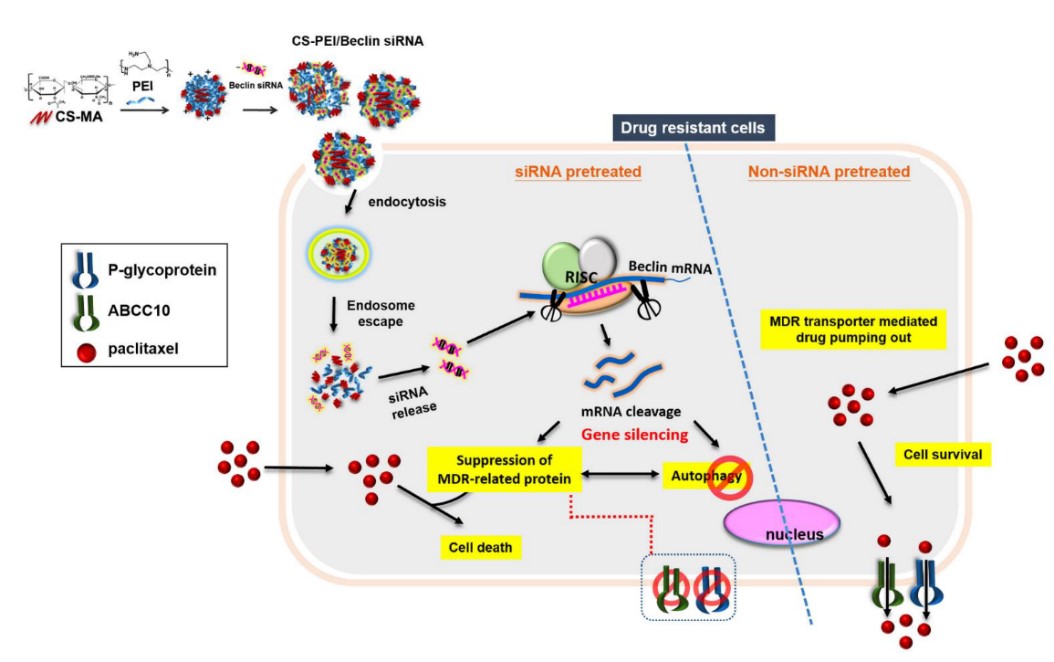
將聚乙烯亞胺(Polyethylenimine, PEI)修飾到硫酸化軟骨素(Chondroitin sulfate, CS),形成一個PEI 接枝CS 之共聚物(簡稱CS-PEI)。PEI是目前市售的一個黃金商品,具高轉染效能的非病毒式基因載體,但是PEI 所擁有的高正電荷密度也對細胞造成很高的毒性。本研究利用低分子量的PEI 接枝到天然的多醣體CS之側鏈上,一來解決臨床未來使用高分子量的PEI對細胞造成的毒性問題;二來以螞蟻雄兵之優勢,利用接掛多條低分子量PEI,使其仍然保留對基因的高轉染率。由於CD44常被發現於腫瘤細胞上,而CS可以辨識細胞膜表面的CD44受體,利用CS-PEI做為基因藥物載體,將增加CS-PEI攜帶之任何基因藥物對細胞表面過度表現CD44的腫瘤或腫瘤幹細胞的靶向性,經由CD44介導的胞飲作用,有效地進入細胞內,提高基因藥物在癌細胞的轉染效能。本研究即以這個低毒性、高轉染的CS-PEI來做為調控自噬作用的Beclin siRNA基因遞送載體;並以紫杉醇(Paclitaxel, PTX)抗藥性的腫瘤細胞株做為細胞模型(如肺癌NCI-H23-TXR),期待藉由抑制細胞的自噬作用,來恢復PTX對腫瘤組織的抑制生長效果。結果發現Beclin siRNA不但抑制Beclin蛋白表現,同時也抑制數個多重抗藥性蛋白的表現,進而促使PTX有效地抑制腫瘤組織的增生。本研究同時也建立一套利用斑馬魚植入腫瘤,快速篩選藥物抑制腫瘤生長的測試平台,未來此平台可延伸至其他腫瘤植入的動物模型。除此,本研究使用的基因載體材料CS-PEI已經獲准台灣專利(I434934)及美國專利(US 8,445,025 B2; US 8,716,399 B2; US 9,050,362 B2),顯見此材料開發具有相當優越的市場開拓新契機。
本校主要研究者之簡介:
本校醫藥暨應用化學系王麗芳教授領導的團隊,集結醫藥化學、生物醫學、奈米醫學、生醫工程、臨床醫學等跨領域專業人才,從化學合成、基因載體的設計、MDR細胞株的建立、自噬作用基因表現、班馬魚腫瘤植入之建立等等,是一個成功的跨系、院、校的成功例子。研究經費由科技部與高雄醫學大學共同支持。
研究聯繫Email: lfwang@kmu.edu.tw ; cchiu@kmu.edu.tw
期刊出處: Molecular Therapy: Nucleic Acids, 2019, 17(9), 477-490.
期刊線上參閱網址:
https://www.cell.com/action/showPdf?pii=S2162-2531(19)30180-5
Polyethyleneimine (PEI) is one of leading cationic polymer for gene delivery because of its high transfection efficiency. However, PEI induced high cytotoxicity due to the positively charged surface characteristics. Herein, we grafted PEI onto chondroitin sulfate (CS) to yield CS-PEI which not only showed transgene efficiency, but reduced PEI cytotoxicity. CD44 is overexpressed in many solid tumor cells. It has been found that CS has the potential to be internalized into cells via CD44-mediated endocytosis. Thus, using CS-PEI as a gene drug delivery system, actively targeting to CD44-overexpressing cancer cells is an ideal approach to enhance transgene efficiency. Multidrug resistance (MDR) is the major obstacle in limitation of therapeutic efficacy of Paclitaxel (PTX). PTX-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer cell line (NCI-H23-TXR) was established and CS-PEI/Beclin-small interfering RNA (siRNA) was constructed to restore sensitivity of PTX against NCI-H23-TXR. Results revealed that knockdown of Beclin simultaneously inhibited MDR-related proteins, and renewed the sensitivity of PTX against NCI-H23-TXR. In vivo study showed that pre-transfection with CS-PEI/Beclin-siRNA followed by PTX treatment decreased the tumor size in NCI-H23-TXR zebrafish xenografts. (Taiwan Patent No. I434934; United States Patent US 8,445,025 B2; US 8,716,399 B2; US 9,050,362 B2)
Main researcher Intro.
Dr. Li-Fang Wang, a professor of Department of Medicinal and Applied Chemistry at Kaohsiung Medical University.
Author Email: lfwang@kmu.edu.tw ; cchiu@kmu.edu.tw
Paper cited from: Molecular Therapy: Nucleic Acids, 2019, 17(9), 477-490.
Paper online website:
https://www.cell.com/action/showPdf?pii=S2162-2531(19)30180-5